Choosing the right batteries for specific conditions is crucial. High and Low Temperature Lithium Batteries are designed for different environments. These batteries differ in performance based on temperature extremes. Understanding this distinction helps in making informed decisions.
High temperature lithium batteries typically excel in hot climates. They offer greater efficiency and longer life. Yet, their performance can drop in cold conditions. On the other hand, low-temperature lithium batteries are ideal for frigid environments. They maintain functionality when temperatures dip. However, their capacity may be limited in warmer areas.
When selecting these batteries, consider the operating conditions. Look at the specifications carefully. Not all batteries are created equal, and some may not perform as expected. Users should reflect on the potential trade-offs. Navigating the options might seem overwhelming, yet making the right choice is essential. Ultimately, consider your specific needs and limitations in battery selection.


When selecting lithium batteries for extreme temperatures, several factors influence their performance. The chemical composition is critical. Different materials respond variably to cold and heat. An electrolyte that performs well in low temperatures may degrade quickly in excessive heat. Battery aging also plays a vital role. Older batteries typically experience reduced efficiency in managing temperature extremes.
Temperature management is essential for longevity. Consider the physical design of the battery. A well-ventilated housing can help dissipate heat. Insulation is crucial in cold environments to maintain optimal temperatures. Look for features that specifically address temperature tolerance. Some batteries have built-in temperature regulation systems. This can prevent overheating during charging.
Tips: Always check the manufacturer's specifications for temperature limits. Test the batteries in real-world conditions before full deployment. Be aware that lithium batteries may not perform equally across all applications. Achieving reliable performance in variable temperatures might require multiple battery types. Testing is key. Evaluate how they react to fluctuations and plan accordingly.
When selecting lithium batteries for extreme temperatures, key specifications must be carefully considered. Battery chemistry is crucial. Some lithium types can withstand high heat, while others perform better in freezing conditions. High temperature batteries often have enhanced electrolyte stability. This is vital in reducing risks of thermal runaway. Meanwhile, low temperature batteries should have optimized electrolyte properties to maintain fluidity.
Capacity and discharge rates are other important factors. High temperature batteries may show decreased capacity under heat stress. Conversely, low temperature batteries often struggle with sluggish discharge. Both scenarios require a balance between energy output and safe operation.
Temperature range specifications in the datasheet are essential. Verify the maximum and minimum operational limits. A common mistake is not paying attention to these figures. Environmental effects can dramatically influence battery performance. Real-world testing often reveals discrepancies between stated and actual performance. Constant review and adjustment are necessary, especially in fluctuating climates.
Lithium battery chemistry varies significantly between high and low-temperature applications. High-temperature lithium batteries often use
lithium cobalt oxide as the cathode material. This type allows for excellent energy density but suffers from reduced life at elevated temperatures.
According to a report by the International Energy Agency (IEA), these batteries can lose about 20% capacity for every 10°C rise in temperature above
25°C.
On the other hand, low-temperature lithium batteries typically utilize
lithium iron phosphate. This chemistry performs better under freezing conditions but offers lower energy density. A study by
Battery University indicates that performance drops sharply in temperatures below
0°C, with discharge rates plummeting by 50% in some applications. Users need to consider both capacity loss
and discharge rates when choosing batteries for extreme environments.
Additionally, heat dissipation is crucial for high-temperature batteries. Poor thermal management may lead to thermal runaway,
a critical safety issue. Ensuring proper design and installation can mitigate risks. In contrast, low-temperature batteries can require pre-conditioning heating to maintain usability.
Hence, both battery types present challenges that users must address effectively.
When selecting high and low temperature lithium batteries, industry standards play a vital role. These standards ensure safety and performance under extreme conditions. Testing parameters include capacity retention, discharge rates, and thermal stability. Manufacturers must adhere to established benchmarks. Meeting these standards indicates reliability.
Testing procedures often involve rigorous assessments. For example, batteries undergo thermal cycling tests. This reveals how they perform in fluctuating temperatures. Additionally, voltage stability is examined. Sometimes, results can be inconsistent. This may raise questions about longevity and efficiency. It’s essential to analyze performance data closely for informed choices.
Industry standards are not perfect. They may fail to account for real-world applications. Environmental conditions can differ widely. Users must consider these factors when choosing batteries. Ultimately, attention to specifications leads to better results. Understanding testing outcomes enhances decision-making in battery selection.
| Parameters | Low Temperature Battery | High Temperature Battery |
|---|---|---|
| Operating Temperature Range | -20°C to 0°C | 40°C to 60°C |
| Capacity Retention at Extreme Temp | > 70% at -20°C | > 80% at 60°C |
| Self-Discharge Rate | < 3% per month | < 5% per month |
| Cycle Life | > 500 cycles | > 300 cycles |
| Weight | Lightweight (e.g., 250g) | Heavier (e.g., 300g) |
| Applications | Cold weather electronics | High temperature environments |
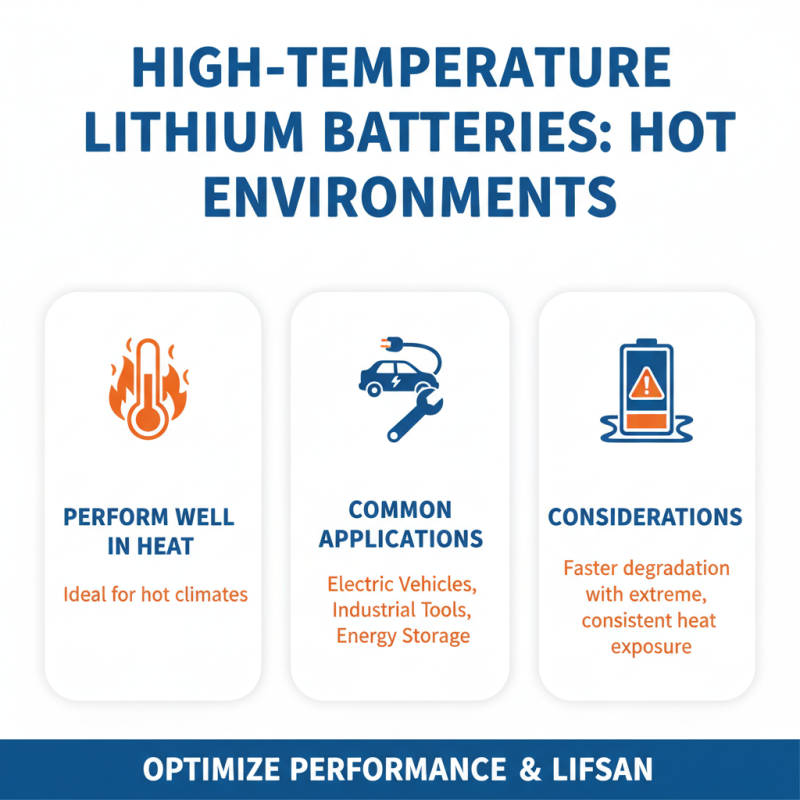
When selecting lithium batteries, temperature ratings are crucial. High-temperature lithium batteries typically perform well in heat. They are suitable for applications in hot environments, like electric vehicles and industrial tools. However, they can degrade faster if consistently exposed to extreme heat.
Low-temperature lithium batteries excel in frigid conditions. They maintain efficiency in cold climates, like winter sports equipment or outdoor sensors. These batteries often struggle in warmth, so careful consideration is needed. It's essential to balance temperature requirements with performance needs.
Pay attention to specific applications. Battery life and efficiency may vary greatly with temperature. Sometimes, datasheets lack detailed temperature performance. This uncertainty requires careful evaluation. Users should also consider the storage and operating conditions to ensure optimal battery selection. A well-chosen battery can make a difference, yet the right choice is not always clear.