0102030405
Major Causes of Lithium-Ion Battery Failures and Maintenance Tips: A Critical Guide to Extending Battery Life
2025-03-01

In today's digital and intelligent age, lithium-ion batteries have become an indispensable energy solution in our lives. From smartphones to electric vehicles, from portable devices to industrial applications, lithium-ion batteries are widely used for their excellent performance and long lifespan. However, despite the many advantages of lithium-ion batteries, they can also face a number of malfunctioning issues that not only affect the performance of the device, but can also lead to safety hazards. Therefore, understanding the main causes of lithium-ion battery failures and how to carry out effective maintenance is crucial to prolonging battery life and ensuring the safe operation of equipment.
Major Causes of Lithium-Ion Battery Failures and Maintenance Guidelines
1.Overcharging: a potential safety hazard
Overcharging is one of the most serious problems facing lithium-ion batteries.
When a battery is charged above its recommended voltage, too much heat is generated, which can lead to an uncontrolled rise in the internal temperature of the battery, which in turn leads to thermal runaway. Thermal runaway not only damages the battery, but can also cause a fire or explosion.
How can I avoid overcharging my battery?
1.To avoid overcharging, it is recommended to use a charger designed for the type of battery and strictly follow the manufacturer's charging guidelines. In addition, chargers with smart charging technology can provide additional safety by automatically cutting off power when the battery is fully charged.
2. Adopt an advanced battery management system (BMS). The optimized design of the BMS can effectively prevent problems such as abnormal voltage and uncontrolled temperature of the Battery Pack by tracking the battery status in real time and optimizing the charging and discharging strategies, thus enhancing the performance of the battery and prolonging its life.
2. Deep discharge: a culprit in shortening battery life
Deep discharging refers to letting a battery almost run out of power before charging it. This behavior significantly reduces the overall life and efficiency of lithium-ion batteries. If a device is draining too quickly or struggling to hold a charge, it's likely due to a deep discharge issue.
How to avoid deep battery discharge?
1. Check the battery level in a timely manner. To minimize the risk of deep discharge, it is recommended to charge the battery when it is down to 20%-30% rather than waiting until it is completely depleted.
2. In addition, choosing a battery with built-in protection circuitry can handle low-voltage situations more effectively, thus extending battery life.
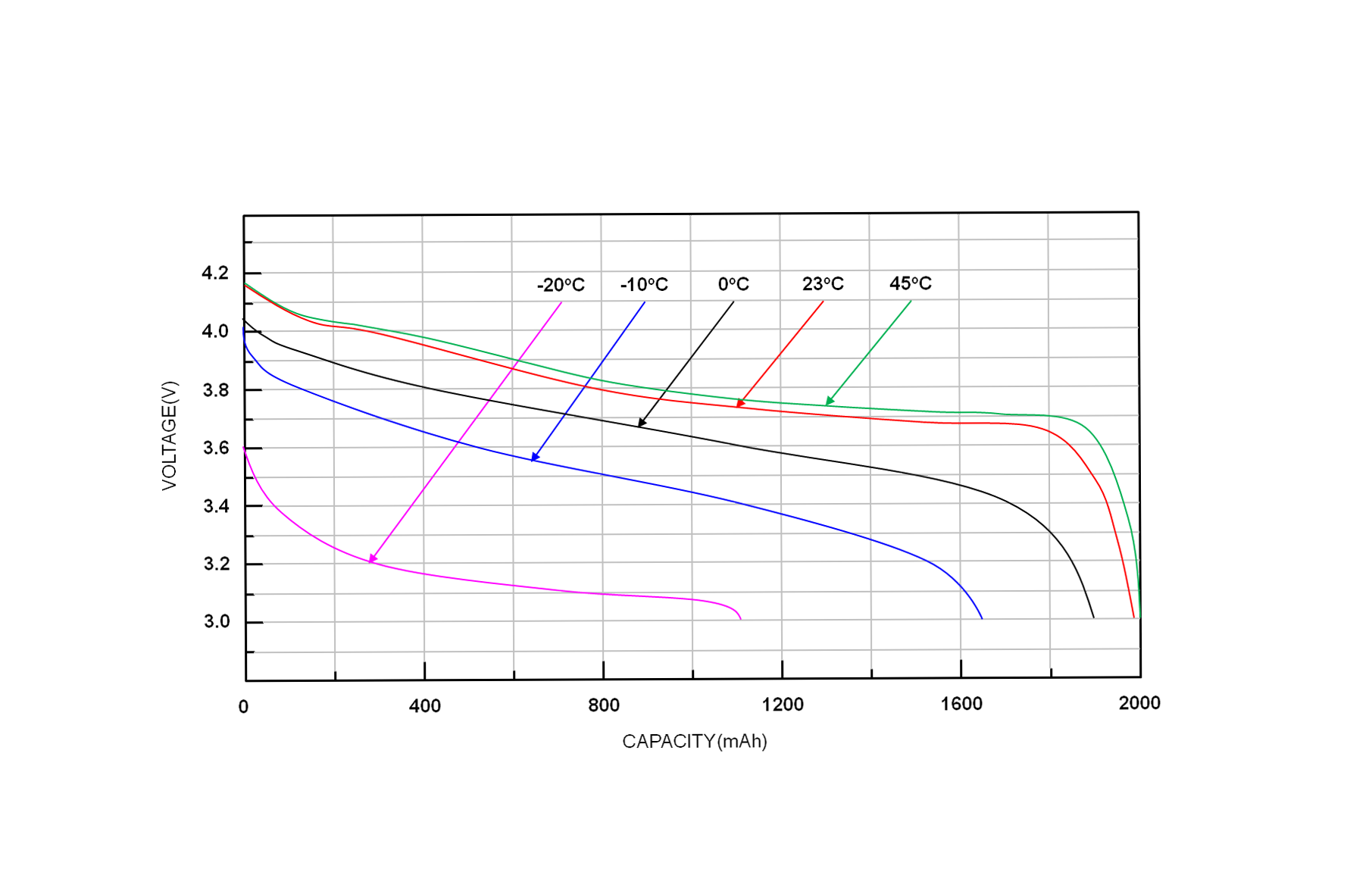
3. Temperature extremes: an invisible killer of performance
Lithium-ion batteries are very sensitive to temperature changes. High temperatures can accelerate chemical reactions within the battery, leading to overheating and potential safety hazards; while low temperatures or extreme cold weather can increase the internal resistance of the battery, reducing performance and efficiency.
How do you make cope with extreme temperatures?
1. To manage battery temperature, it is recommended that batteries be used and stored in cool, dry environments, avoiding exposure of the device to direct sunlight or high temperatures.
2. For applications that require operation in extreme environments, customized lithium-ion battery packs with built-in heating or cooling mechanisms can be designed.
4. Physical damage: risk of accidental impact
Physical damage to lithium-ion batteries, such as puncture, dropping or crushing, may destroy the internal structure of the battery, leading to short circuits, electrolyte leakage and even thermal runaway. Even minor physical shocks may jeopardize the integrity and safety of the battery.
How can I reduce the risk of physical damage to my batteries?
1. To avoid physical damage, it is recommended that battery packs be designed with robust mechanical protection, such as the use of shock-absorbing or protective enclosures, and that portable battery packs be handled and stored properly.
2. Regular inspection of batteries for signs of wear or damage, timely detection and resolution of problems can effectively avoid potential risks.